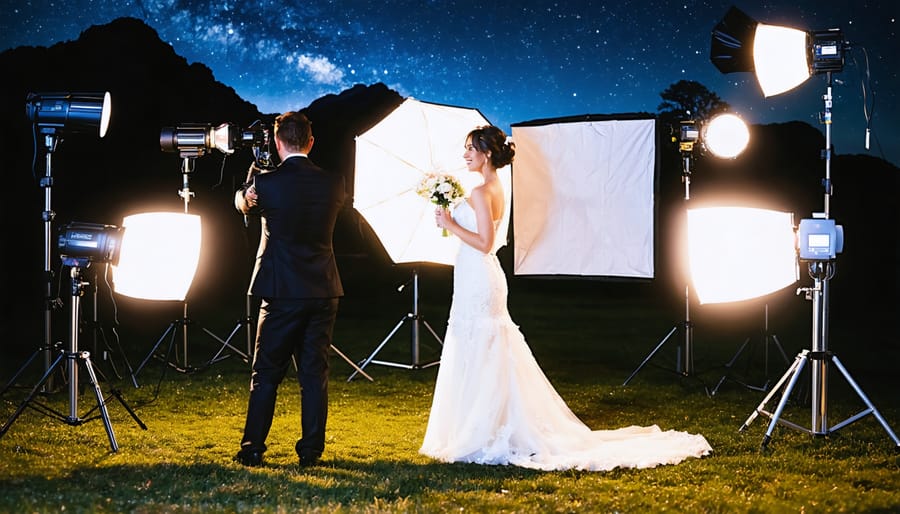
Battery-powered photography lights have revolutionized the way we capture images on location, freeing photographers from the constraints of power outlets and studio setups. Whether you’re shooting a wedding in a remote chapel or capturing fast-paced events in challenging environments, these portable lighting solutions have become indispensable tools in modern photography.
The perfect balance of power, portability, and reliability makes battery-powered lights essential for photographers who demand professional results anywhere, anytime. From compact speedlights to powerful strobe systems, today’s battery-operated lighting equipment offers unprecedented creative control while maintaining the mobility that contemporary photography demands.
As technology advances, we’re seeing remarkable improvements in battery life, recycle times, and output consistency – factors that were once major limitations of portable lighting systems. These innovations have opened new possibilities for photographers, enabling them to tackle challenging lighting situations with confidence and achieve studio-quality results in any location.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about battery-powered photography lights, from choosing the right system for your needs to maximizing battery life and maintaining your equipment for optimal performance. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or just starting to explore off-camera lighting, understanding these portable lighting solutions is crucial for elevating your photography to the next level.
Understanding Your Battery-Powered Photography Lights
Common Battery Types in Photography Lights
Photography lights commonly use several types of batteries, each with distinct advantages. Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries are the most popular choice, offering an excellent balance of power capacity and weight. They maintain consistent output throughout their charge cycle and can be recharged hundreds of times, making them cost-effective in the long run.
Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) batteries represent another reliable option, particularly for photographers who prefer standard AA or AAA sizes. While they have a lower energy density than Li-ion, they’re more affordable and less prone to thermal issues. However, they do exhibit a gradual voltage drop during use, which can affect light output consistency.
Some premium lighting systems use proprietary battery packs, often based on lithium polymer (LiPo) technology. These offer high power density and fast charging capabilities but typically come at a premium price point.
Alkaline batteries, while readily available, are generally only recommended as backup options due to their short life span and inconsistent power output in high-drain devices like photography lights. They’re best reserved for emergency situations when rechargeable options aren’t available.

Power Consumption Patterns
Understanding how different light settings affect battery consumption can help you maximize your shooting time. At full power, most battery-powered lights will drain significantly faster, typically lasting 200-300 flashes. However, when operating at 1/4 power, you might get 800-1000 flashes from the same battery charge.
Continuous lighting modes are particularly demanding on batteries, often depleting them within 1-2 hours of constant use at full brightness. By reducing the output to 50%, you can typically extend the runtime to 3-4 hours. Color temperature adjustments also impact battery life, with bi-color LEDs consuming more power when set to intermediate color temperatures.
Rapid-fire shooting can be especially taxing on batteries due to the constant recycling of the capacitors. To optimize battery life during intense shooting sessions, consider using lower power settings and allowing brief recovery periods between bursts. Modern lights often include power-saving features like auto-shutdown and brightness memory, which can help extend battery life during longer shoots.
Remember that ambient temperature affects battery performance – cold conditions can reduce battery efficiency by up to 30%, while excessive heat might trigger protective shutdowns.

Maximizing Battery Performance
Pre-Shoot Battery Preparation
Proper battery preparation is crucial for a successful photo shoot. Start by fully charging all your batteries at least 24 hours before your session. This gives you time to identify any batteries that aren’t holding a charge well and arrange backups if needed. When organizing photography equipment, keep fresh batteries separate from used ones using clearly marked cases or compartments.
Test each battery’s performance by running your lights at full power for 30 seconds. Monitor the battery level indicator – if it drops significantly during this brief test, set that battery aside for less demanding situations. For critical shoots, always pack at least twice the number of batteries you think you’ll need.
Consider the shooting environment’s temperature, as cold conditions can significantly reduce battery life. If shooting in cold weather, keep spare batteries in an insulated pocket close to your body. For extended sessions, implement a rotation system where you swap batteries before they’re completely drained, which helps preserve their long-term health.
Label your batteries with purchase dates and keep a log of their usage patterns. This helps track their performance over time and anticipate when replacements might be needed. Remember to store batteries at around 40% charge if you won’t be using them for an extended period, as this helps maintain their overall lifespan and reliability.
During-Shoot Management
Managing your battery-powered lights during a shoot requires strategic thinking to maximize their performance and longevity. Start by fully charging all batteries before your session and always pack spares. During the shoot, use the modeling light sparingly – while it’s helpful for previewing your lighting setup, it’s a significant battery drain.
When working with multiple lights, consider powering up only the units you’re actively using. This approach not only conserves battery life but also helps you maintain better control over your lighting setup. Keep an eye on your battery indicators and swap them out when they reach about 25% capacity to avoid any sudden power loss during crucial shots.
Temperature management is crucial for battery efficiency. In cold conditions, store spare batteries in an inside pocket to keep them warm, as cold temperatures can significantly reduce their performance. Conversely, avoid leaving batteries in direct sunlight or hot environments during outdoor shoots.
To extend battery life during longer sessions, adjust your power settings wisely. Using lower power settings when possible not only saves battery life but also allows for faster recycle times. If you’re shooting in bursts, consider using your lights at 75% power instead of full power – you’ll often get similar results with significantly better battery efficiency.
Remember to power down your lights during extended breaks between shots. Even in standby mode, these units continue to draw power, and those small savings can add up over a long shoot day.
Post-Shoot Care
Proper care of your battery-powered photography lights after a shoot is crucial for extending their lifespan and maintaining optimal performance. Start by allowing your lights to cool down completely before storing them. Remove the batteries if you won’t be using the lights for an extended period, as this prevents potential battery leakage that could damage your equipment.
Clean your lights gently with a soft, dry microfiber cloth to remove any dust or fingerprints. Pay special attention to the LED panels and diffusion materials, as accumulated dirt can affect light output. For stubborn marks, use a slightly damp cloth, but never spray cleaning solutions directly onto the equipment.
Following these essential maintenance tips will help preserve your investment. Store your lights in a cool, dry place, ideally in their original cases or dedicated padding. Consider using silica gel packets in your storage containers to prevent moisture buildup, especially if you live in a humid climate.
Check the battery contacts periodically for signs of corrosion and clean them if necessary. Keep spare batteries in a separate container, and always organize them by charge level to avoid mixing fresh and depleted cells. Remember to fully charge your batteries before storing them for long periods, as this helps maintain their capacity and extends their overall lifespan.
Troubleshooting Common Battery Issues
Battery Memory Effect
The battery memory effect, once a significant concern with older nickel-cadmium (NiCd) batteries, is less prevalent in modern photography lighting equipment. However, understanding this phenomenon can help you better maintain your gear. Battery memory occurs when batteries are repeatedly charged before being fully depleted, causing them to “remember” shorter charge cycles and reducing their effective capacity.
Fortunately, most contemporary battery-powered photography lights use lithium-ion (Li-ion) or lithium polymer (LiPo) batteries, which don’t suffer from traditional memory effect. These modern batteries can be charged at any time without degrading their capacity, making them more convenient and reliable for photography work.
Despite this improvement, it’s still good practice to occasionally fully discharge and recharge your batteries. This process, known as battery conditioning, helps maintain accurate battery level indicators and optimal performance. For professional shoots, always carry fully charged backup batteries and avoid waiting until your lights are completely drained before switching.
To maximize battery life and performance, store your photography lights at around 40% charge when not in use for extended periods. Avoid exposing batteries to extreme temperatures, as this can affect their capacity and longevity. Many photographers keep their batteries in a dedicated case with their lighting kit, protecting them from environmental factors while ensuring they’re always ready for the next shoot.
Cold Weather Performance
Cold weather can significantly impact battery performance in photography lights, often reducing their efficiency and runtime by up to 50% in freezing conditions. To maintain optimal performance during winter shoots or cold-weather assignments, it’s essential to implement several practical strategies.
Keep spare batteries close to your body, preferably in an inside pocket of your jacket, where your natural body heat will help maintain their temperature. This simple technique can dramatically improve their performance when you need to swap them out. When shooting, try to keep the light unit itself as warm as possible between shots by storing it in an insulated bag.
Consider using lithium-ion batteries instead of alkaline ones for cold weather shoots, as they generally perform better in low temperatures. Many professional photographers carry battery hand warmers or specialized battery pouches designed for cold weather use. These accessories can help maintain battery temperature and extend their useful life during challenging conditions.
Monitor your battery levels more frequently in cold conditions, as the charge indicator might not be as accurate when temperatures drop. It’s also wise to pack more spare batteries than you typically would for a regular shoot – a good rule of thumb is to bring twice your normal backup supply when working in cold environments.
Remember to allow your equipment to gradually warm up to room temperature before charging to prevent condensation damage. Sudden temperature changes can be just as harmful as the cold itself.
Long-Term Battery Care and Storage
Storage Temperature and Conditions
Proper storage of your battery-powered photography lights isn’t just about tossing them in a drawer – it’s crucial for maintaining performance and extending their lifespan. Different battery types require specific storage conditions, and implementing smart storage solutions can make a significant difference.
For lithium-ion batteries, aim to store them at around 40% charge in a cool, dry environment between 59-77°F (15-25°C). Avoid extreme temperatures, as heat can permanently damage the cells, while cold conditions temporarily reduce capacity. Never store them fully charged or completely depleted.
Nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries prefer similar temperature ranges but can be stored fully charged. However, they self-discharge more quickly than lithium-ion, so check and recharge them every few months.
Alkaline batteries should be kept in their original packaging or a plastic case, away from metal objects that could cause short circuits. Store them at room temperature and avoid mixing new and old batteries.
For all battery types, maintain moderate humidity levels (35-45%) in your storage area. Use silica gel packets in your storage containers to absorb excess moisture. Keep batteries separated from each other and away from direct sunlight. Regular inspection for signs of damage or leakage is essential, especially before extended storage periods.
Remember to rotate your battery stock, using older batteries first, and always remove batteries from devices during long-term storage to prevent potential damage from leakage.

Replacement Timing
Knowing when to replace batteries in your photography lights is crucial for avoiding unexpected failures during shoots. The most reliable indicator is the battery level display, typically shown through LED indicators or digital displays on modern units. However, don’t rely solely on these indicators – pay attention to how your light performs during use.
Watch for signs like decreased maximum power output, longer recycle times between flashes, or inconsistent light output. If your usual power setting isn’t producing the same brightness, or if the light takes noticeably longer to recharge between shots, it’s likely time for fresh batteries.
For rechargeable batteries, keep a log of charging cycles. Most professional-grade batteries maintain optimal performance for 300-500 charge cycles. After this point, their capacity begins to diminish notably. If you’re using disposable batteries, track their usage time – most alkaline batteries provide 2-4 hours of continuous use at full power.
A practical approach is to mark your batteries with the date you started using them. This helps track their age and usage patterns. Always carry spare batteries during shoots, and consider replacing them preemptively before important assignments. It’s better to change batteries slightly early than risk them failing during a crucial moment.
For consistency in professional work, consider replacing rechargeable batteries annually, regardless of usage, to maintain peak performance and reliability.
Battery-powered photography lights have revolutionized the way we capture images, offering unprecedented flexibility and creative freedom. Throughout this guide, we’ve explored the essential aspects of these versatile tools, from choosing the right batteries to implementing effective maintenance routines.
Remember that proper battery care is not just about extending the life of your equipment—it’s about ensuring reliability when you need it most. By following the recommended charging practices, storing batteries correctly, and monitoring their performance, you can avoid unexpected power failures during critical shoots.
The key takeaways are clear: always carry backup batteries, maintain a regular charging schedule, and pay attention to temperature conditions during both use and storage. Quality battery-powered lights, when properly maintained, can serve you reliably for years, making them a worthwhile investment for any photographer.
Consider implementing a battery management system that works for your specific shooting style and frequency. Whether you’re a wedding photographer requiring all-day reliability or a studio photographer with more controlled power needs, having a solid battery care routine is crucial.
As technology continues to advance, battery-powered photography lights will only become more efficient and powerful. By establishing good habits now, you’ll be well-positioned to make the most of your current and future lighting equipment, ensuring your creative vision is never compromised by power issues.