
Step into the future of visual storytelling with 4K 360-degree cameras, the revolutionary tools transforming how we capture and create immersive VR experiences. These cutting-edge devices pack multiple high-resolution sensors into a compact form factor, capturing every angle simultaneously in stunning 4K clarity. Whether you’re a professional content creator designing virtual tours, a filmmaker pushing creative boundaries, or an adventurer documenting expeditions, 360-degree cameras offer unparalleled creative freedom and technical capabilities that were unimaginable just a few years ago.
The marriage of 4K resolution with omnidirectional capture creates possibilities that extend far beyond traditional photography and videography. Real estate professionals can now showcase entire properties in a single take, while event photographers capture every moment without missing a single reaction. Virtual reality developers leverage these cameras to build authentic, engaging environments that transport viewers into completely new worlds.
The technology behind these cameras represents a perfect convergence of advanced optics, sophisticated stitching algorithms, and precise sensor synchronization – all working seamlessly to deliver crystal-clear, sphere-shaped content that viewers can explore from any angle. As the demand for immersive content continues to surge, 4K 360-degree cameras stand at the forefront of this visual revolution, empowering creators to craft experiences that don’t just show a scene, but invite audiences to step inside it.
Why 4K Resolution Matters in 360-Degree VR
The Math Behind VR Resolution
When it comes to VR resolution, understanding pixels per degree (PPD) is crucial. In a 360-degree environment, a 4K image (3840 x 1920 pixels) is stretched across your entire field of view. For typical VR headsets with a 100-degree horizontal viewing angle, this translates to roughly 38 pixels per degree (3840 ÷ 100).
This math becomes particularly important when considering human vision. Our eyes can distinguish details up to about 60 PPD in optimal conditions, which means current 4K 360-degree cameras still fall short of matching human visual acuity. To achieve true-to-life detail across the entire 360-degree sphere, we’d theoretically need around 21,600 x 10,800 pixels (approximately 233 megapixels).
However, since most viewers focus on a specific area rather than the entire sphere simultaneously, 4K resolution can still provide a satisfactory viewing experience. The key is understanding that while the total pixel count sounds impressive, it’s being distributed across a much larger viewing area than traditional flat displays.
Visual Quality Comparison: 2K vs 4K in 360 VR
When comparing 2K and 4K footage in 360 VR environments, the differences become particularly noticeable during immersive viewing. In 2K resolution, viewers might observe pixelation when looking closely at objects, especially text or detailed patterns. This effect becomes more pronounced when users zoom in or focus on specific areas of the scene.
4K footage, on the other hand, maintains clarity even when viewers lean in to examine details. Take a cityscape scene, for example – with 2K, distant buildings might appear somewhat blocky, while 4K preserves crisp architectural details and clear window definitions. Similarly, in nature shots, 4K captures fine textures like tree leaves and grass blades that might appear muddied in 2K.
The distinction becomes even more apparent when viewing through VR headsets, where the screen is mere inches from your eyes. While 2K footage can still deliver a satisfactory experience for casual viewing, professional productions benefit significantly from 4K’s enhanced detail retention, particularly in scenes with complex textures, motion, or text overlays. This quality difference directly impacts viewer immersion and the overall professional polish of the final product.
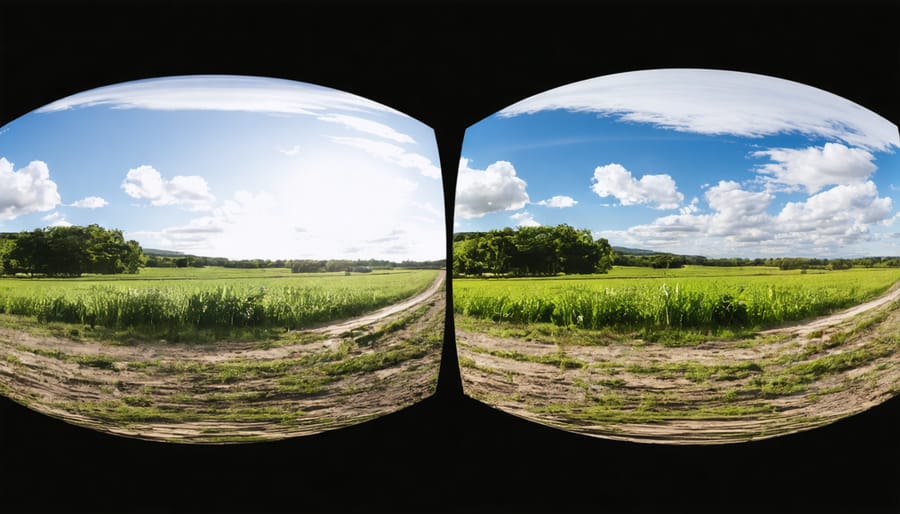

Essential Features of 4K 360 Cameras for VR
Sensor Configuration and Stitching Technology
At the heart of modern 360-degree camera technology lies an intricate system of multiple image sensors working in perfect harmony. Most 4K 360-degree cameras utilize dual fisheye lenses, each paired with its own high-resolution sensor, typically capturing 180-degree fields of view that overlap slightly for seamless stitching.
The magic happens when these separate video feeds are combined through sophisticated stitching algorithms. Think of it like creating a digital quilt – the camera’s processor takes the overlapping edges of each sensor’s footage and blends them together in real-time. Modern stitching technology has evolved to handle various challenges, including exposure differences between sensors and moving subjects that cross the stitch lines.
The quality of this stitching process is crucial for immersive VR experiences. The best 4K 360 cameras employ advanced pixel-matching algorithms and motion compensation to ensure that the seam between sensors remains invisible, even in challenging conditions like low light or fast movement.
For optimal results, most cameras position their sensors back-to-back with precise alignment. This configuration minimizes parallax errors – those subtle misalignments that can occur when capturing objects close to the camera. Some premium models even include additional sensors for better coverage and reduced blind spots, though this requires more sophisticated stitching algorithms to maintain that seamless spherical view.
Frame Rates and Motion Handling
Frame rate selection in 4K 360-degree cameras plays a crucial role in creating immersive VR experiences that are both comfortable and visually engaging. Most modern 360 cameras offer multiple frame rate options, typically ranging from 24fps to 60fps, with some high-end models capable of reaching 120fps for slow-motion capture.
For standard VR content, shooting at 60fps provides the sweet spot between smooth motion and manageable file sizes. This frame rate effectively reduces motion blur and minimizes the risk of VR sickness, particularly when viewers are moving their heads to explore the scene. When capturing fast-moving subjects or action sequences, higher frame rates become especially valuable as they help maintain clarity and reduce strobing effects.
However, it’s worth noting that lower frame rates like 24fps or 30fps can still be appropriate for certain situations. These traditional frame rates create a more cinematic feel and require less storage space, making them suitable for dialogue scenes or relatively static environments. Some creators even mix frame rates within their projects, using higher rates for action sequences and lower rates for casual scenes.
Motion handling capabilities also depend on the camera’s processing power and stabilization features. Advanced models incorporate sophisticated image processing algorithms that work alongside higher frame rates to deliver smoother footage, even in challenging shooting conditions.
Storage and Data Management
Managing storage for 4K 360-degree footage can be quite demanding, as these files are significantly larger than traditional video formats. A single minute of 4K 360 footage typically requires between 1-2GB of storage space, depending on your camera’s compression settings and frame rate.
To effectively manage your storage needs, consider investing in high-capacity SD cards (128GB or larger) with fast write speeds. Look for cards rated V30 or higher to handle the data throughput required for 4K 360 recording. It’s always wise to carry multiple cards during shoots, as you’ll be surprised how quickly they fill up.
For long-term storage, external SSDs or HDDs are essential. A 4TB external drive can store approximately 30-40 hours of 4K 360 footage. Consider implementing a reliable backup system using the 3-2-1 rule: three copies of your data, stored on two different types of media, with one copy kept off-site.
When it comes to file management, organize your footage using a consistent naming convention and folder structure. Many creators sort their files by date, project, or location. Consider using specialized media management software to help catalog and tag your 360 footage, making it easier to locate specific clips when needed.
For efficient editing workflow, consider using proxy files – lower-resolution versions of your footage that put less strain on your computer during the editing process. You can always link back to the original high-resolution files for final export.
Shooting Techniques for VR Environments
Camera Placement and Height
The placement and height of your 4K 360-degree camera can make or break your VR experience. For optimal results, position your camera at eye level – typically between 5’5″ and 5’8″ from the ground. This natural viewing height helps prevent viewer discomfort and creates a more immersive experience.
When mounting your camera, use a slim monopod or selfie stick rather than a traditional tripod. This minimizes the camera’s footprint in your final footage, as wider supports can create noticeable distortions in the lower hemisphere of your 360-degree view. Remember to position yourself at least 6 feet away from the camera during recording to avoid appearing unnaturally large in the final footage.
For indoor shoots, place the camera in the center of the room whenever possible. This provides equal distance to walls and objects, resulting in better depth perception and spatial awareness for viewers. In outdoor settings, look for clear areas without overhanging obstacles that might create awkward blind spots in your footage.
Consider your audience’s viewing position – will they be standing or seated? For seated experiences, lower the camera height to approximately 4 feet. For action shots or dynamic scenes, you might experiment with different heights, but always keep in mind that extreme angles can cause viewer disorientation in VR environments.
Avoid placing the camera too close to walls or objects – maintain at least a 3-foot clearance to prevent distortion in the stitching process. This spacing also helps maintain proper perspective and depth in your final footage.
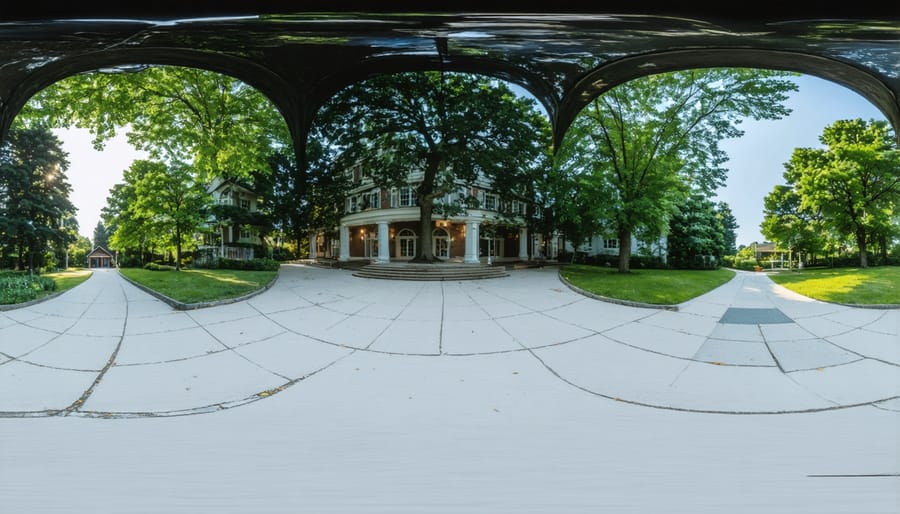

Lighting Considerations
Mastering lighting in 360-degree environments presents unique challenges compared to traditional photography. Unlike standard cameras where you can position lights outside the frame, every angle is captured in 360-degree footage, requiring careful consideration of your lighting techniques.
Natural light can be your best friend when shooting outdoors, but timing is crucial. The golden hours (just after sunrise or before sunset) provide warm, even illumination that works wonderfully for 360-degree captures. During harsh midday sun, look for locations with partial coverage, like tree canopies, to create balanced lighting across your scene.
For indoor shoots, consider using multiple small LED panels positioned at equal distances from the camera. This creates uniform illumination while minimizing the visibility of light sources in your final footage. Remember to hide lights behind natural objects in the scene, such as furniture or architectural elements, whenever possible.
One effective approach is to use bounce lighting by directing lights toward walls or ceilings. This creates soft, diffused illumination that appears more natural in your 360-degree environment. When shooting in mixed lighting conditions, white balance becomes particularly important – consider using a gray card reference visible in one direction of your shot for easier post-production adjustment.
For situations where hiding lights isn’t possible, plan to remove them in post-production using content-aware tools, but remember this adds time to your workflow.
Movement and Stabilization
Capturing smooth, professional-looking 360-degree footage requires mastering both camera handling and stabilization techniques. The key to achieving fluid motion lies in understanding how 360-degree cameras process movement differently from traditional cameras.
When shooting handheld, use a specialized 360-degree camera grip or monopod to minimize unwanted shake. These tools provide a stable base while keeping your hands away from the camera’s field of view. For walking shots, adopt a heel-to-toe walking technique and bend your knees slightly to act as natural shock absorbers.
Many modern 4K 360-degree cameras come equipped with built-in electronic image stabilization (EIS) or gyroscopic stabilization systems. While these features help smooth out minor movements, mastering pro-level VR techniques will significantly enhance your footage quality.
For more dynamic shots, consider investing in a motorized gimbal specifically designed for 360-degree cameras. These gimbals compensate for multi-axis movement, ensuring your horizon stays level even during complex camera movements. Some popular options include invisible selfie sticks that automatically remove themselves from the final footage.
Remember to plan your movements carefully, as sudden direction changes can disorient viewers in VR environments. Keep your movements slow and purposeful, allowing viewers to naturally adjust to perspective shifts while maintaining immersion in the 360-degree experience.
Post-Production Workflow
Stitching and Color Correction
Creating seamless 360-degree footage requires sophisticated stitching and color correction techniques to ensure a professional final product. Most 4K 360 cameras come with dedicated software that handles the initial stitching process, combining footage from multiple lenses into a cohesive spherical video.
Popular stitching software like PTGui and Mistika VR offer advanced control over stitch lines and blending, helping eliminate visible seams where the camera’s fields of view overlap. For best results, shoot with adequate overlap between lenses and maintain consistent lighting conditions across all angles.
Color correction in 360-degree footage presents unique challenges because you’re working with a wraparound image. Traditional color grading techniques need to be adapted to ensure consistent color temperature and exposure across the entire sphere. Software solutions like Adobe Premiere Pro and DaVinci Resolve now include specialized tools for 360-degree footage, allowing you to make adjustments while previewing the content in its spherical form.
Pay special attention to the zenith (top) and nadir (bottom) points of your footage, as these areas often require additional correction due to lighting differences. Some creators opt to shoot with a slightly higher exposure to retain detail in shadows, then adjust in post-production.
When working with multiple cameras in an array setup, color matching becomes crucial. Using color charts during filming and batch processing in your editing software helps maintain consistency across all cameras. Remember to export your final footage in equirectangular format for compatibility with most VR platforms and players.
Export Settings for VR Platforms
When exporting your 360-degree footage for VR platforms, optimizing your settings is crucial for the best viewing experience. For Meta Quest (formerly Oculus) devices, export your footage at 4096×4096 resolution with H.264 encoding and a bitrate between 30-60 Mbps. Enable high-profile encoding and maintain a constant frame rate of 30fps for smooth playback.
YouTube VR requires slightly different specifications. Export your content at 4K resolution (3840×2160) for each eye in an over-under format. Use the H.264 codec with a bitrate of at least 45 Mbps, and ensure your metadata tags are properly set for 360-degree playback. YouTube automatically processes the video for VR viewing once uploaded with correct settings.
For Steam VR and other PC-based platforms, aim for maximum quality with 5.7K resolution if your camera supports it. Use the H.265 (HEVC) codec for better compression while maintaining quality, with a bitrate of 50-80 Mbps. Remember to export in equirectangular projection format, which is the standard for most VR platforms.
When exporting for mobile VR experiences, consider file size limitations. A resolution of 3840×1920 usually offers the best balance between quality and performance. Keep the bitrate between 25-35 Mbps to ensure smooth streaming while maintaining good visual fidelity.
For all platforms, ensure your audio is exported in spatial audio format (ambisonics) when available, as this greatly enhances the immersive experience. Export in MP4 container format for maximum compatibility, and always test your content on the target platform before final distribution.
The rise of 4K 360-degree cameras has fundamentally transformed the landscape of virtual reality content creation, offering unprecedented opportunities for immersive storytelling and interactive experiences. As we’ve explored throughout this article, these sophisticated devices combine high-resolution capture capabilities with complete spatial coverage, making them invaluable tools for VR content producers, filmmakers, and creative professionals.
The ability to capture crystal-clear 4K footage in all directions simultaneously has opened new doors for virtual tours, immersive documentaries, and interactive educational content. Real estate professionals can now offer potential buyers complete virtual walkthroughs of properties, while tourism operators can provide prospective visitors with authentic previews of destinations and experiences.
Looking ahead, the future of 4K 360-degree cameras appears incredibly promising. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even higher resolutions, improved low-light performance, and more sophisticated stitching algorithms. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning will likely enhance image stabilization and automated post-processing capabilities, making these cameras even more accessible to creators at all skill levels.
The growing demand for VR content across industries – from entertainment and education to healthcare and corporate training – suggests that 4K 360-degree cameras will become increasingly essential tools in content creation workflows. As VR headsets become more commonplace and audiences seek more immersive experiences, the ability to create high-quality 360-degree content will become a crucial skill for creative professionals.
Whether you’re a professional filmmaker, content creator, or enthusiast looking to explore new creative possibilities, investing in a 4K 360-degree camera today means positioning yourself at the forefront of the virtual reality revolution. The technology has matured to a point where it offers reliable performance and exceptional quality, making now an excellent time to dive into the world of immersive content creation.






















